Vitamin D is an integral part of our health. This vitamin, which is also labelled as a hormone due to its vital role in the metabolism of human body, was initially considered to have role in bone health only. As per daily advances, vitamin D is essential for bone health, reduces inflammation, facilitates the immune system to fight off infection and plays a role in preventing cancer.
The body produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. This is the primary source of gaining appropriate levels of this vitamin. It is also available in the form of oral supplements. (1)
1. Sun exposure
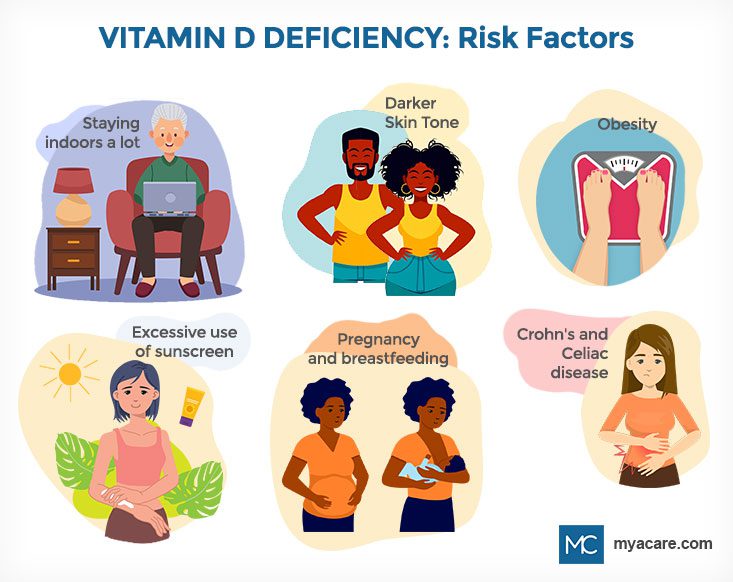
Vitamin D levels in the body can be boosted with sufficient exposure to sunlight. The cholesterol receptors in the skin absorb UV radiation from the sunlight and convert to a precursor of vitamin D. Individuals that spend more time indoors, cover their face and body while going out and live in regions with decrease exposure to sunlight may have reduced levels of vitamin D in their body. (2)
2. Diet low in vitamin D
Vitamin D is an animal-based vitamin which can be deficient in people who follow specific diets that exclude animal-based food. Strict vegetarians often miss vitamin D in their diets as it is
mostly available in fish, egg yolks, cod liver oil and beef liver. Poverty is a significant aspect in Pakistan which deprives women the access to a proper and healthy diet. (3)
3. Renal diseases
The kidneys convert vitamin D to its active form. Renal diseases impair this conversion and deplete the body to utilize its vitamin D. According to research, about 80 percent of individuals with chronic kidney disease have vitamin D deficiency due to failure of adequate renal function. (4)
4. Gastrointestinal diseases
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin which is significantly taken from exogenous sources. Diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, ulcerative colitis and pancreatic insufficiency impair the absorption of this vitamin and ultimately leads to its deficiency. (5)
What problems do women with vitamin D deficiency face?
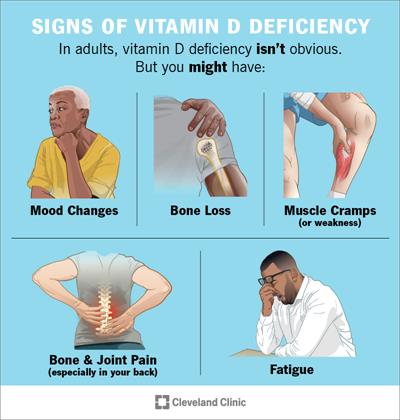
1. Bone and joint pains
Women suffering from vitamin D deficiency have complains of joint pains and easy fatiguability. This is attributed to the fact that vitamin D increases bone density and promotes healthy growth. Reduced levels of this component decrease bone density and leads to its fragility and causes bone and joint pain. (6)
2. Increased frequency of infections
Vitamin D is considered to boost immunity and fight off infections in the body. Its deficiency leads to repeated infections, especially viral illnesses. Many studies show that low vitamin D levels are associated with respiratory infections like influenza, pneumonia and sepsis. (7)
3. Bone weakness and fractures
Vitamin D plays a significant role in bone metabolism and its deficiency leads to bone wasting and weakness. The daily wear and tear of bone cells increases, and minor trauma leads to major damage. This is greatly seen in menopausal women where low estrogen levels have an additional role to play. (8)
4. Hair fall
Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory properties and plays an important role in keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation. Lack of this significant vitamin can lead to depletion in hair growth and excessive hair growth. (9)
Recommended dose of vitamin D supplementation for women
The daily intake of vitamin D supplementation depends on various factors. The recommended dose for females is 600 IU daily for age 14-70 years and 800 IU daily after 70 years. (10) This requirement may increase during pregnancy and lactation depending on pre-existing deficit.
Factors that may affect these doses are age, exposure to sunlight, lifestyle, dietary vitamin D intake, underlying renal of gastrointestinal diseases and obesity.
Vitamin D plays an integral role in the metabolism of our body and the deficiency of this vitamin alters important functions. Many women in Pakistan are predisposed to this deficiency and present with signs and symptoms that worsen during pregnancy and after menopause. Women in this region have adequate exposure to sunlight but as majority of the population lies below the poverty line, their access to rich and nutritious food is limited.
To overcome this, awareness programs regarding vitamin D deficiency and supply of supplementation in health clinics can help in the prevention of adversities. Another important factor is to encourage the consumption of vitamin D rich foods and supplements from a young age, especially in the reproductive years as this can prevent the subsequent post-menopausal infestations.
References
1. Vandevijvere, S., Amsalkhir, S., Van Oyen, H., & Moreno-Reyes, R. (2012). High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in pregnant women: a national cross-sectional survey.
2. Lips, P., van Schoor, N. M., & de Jongh, R. T. (2014). Diet, sun, and lifestyle as determinants of vitamin D status. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1317(1), 92-98.
3. Lamberg-Allardt, C. (2006). Vitamin D in foods and as supplements. Progress in biophysics and molecular biology, 92(1), 33-38.
4. Williams, S., Malatesta, K., & Norris, K. (2009). Vitamin D and chronic kidney disease. Ethnicity & disease, 19(4 Suppl 5), S5.
5. Bikle, D. D. (2007). Vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency in gastrointestinal disorders. Journal of bone and mineral research, 22(S2), V50-V54.
6. Holick, M. F. (2003, December). Vitamin D deficiency: what a pain it is. In Mayo clinic proceedings (Vol. 78, No. 12, pp. 1457-1459). Elsevier.
7. Watkins, R. R., Lemonovich, T. L., & Salata, R. A. (2015). An update on the association of vitamin D deficiency with common infectious diseases. Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 93(5), 363-368.
8. Busse, B., Bale, H. A., Zimmermann, E. A., Panganiban, B., Barth, H. D., Carriero, A., … & Ritchie, R. O. (2013). Vitamin D deficiency induces early signs of aging in human bone, increasing the risk of fracture. Science translational medicine, 5(193), 193ra88-193ra88.
9. Saini, K., & Mysore, V. (2021). Role of vitamin D in hair loss: A short review. Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 20(11), 3407-3414.
10. Ross, A. C., Manson, J. E., Abrams, S. A., Aloia, J. F., Brannon, P. M., Clinton, S. K., … & Shapses, S. A. (2011). The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: what clinicians need to know. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 96(1), 53-58.





















