Contraception is referred to as a method to prevent unwanted pregnancy. There are various options available for women. Contraception enables couples to imply the concept of family planning. The choice of contraception depends on certain personal preferences like frequency of intercourse, number of partners, the desire to have children in future, prevention of certain transmissible diseases, affordability and diseases of the reproductive system. It enables individuals to safeguard their health along with enjoying the pleasures of life.
There are various modes of contraception available these days and they are offered as per the needs of the user, but the success rates may vary. The most common methods are oral contraceptives, barrier contraception, intrauterine system, intrauterine devices, hormone implants and surgery.
The merits and demerits of these methods are described below.
- Combined oral contraceptive pills
Oral contraceptive pills are composed of hormones estrogen and progestin which are naturally produced by the ovaries. Progestin only pills are also available. This is a reliable mode of contraception exclusive for women, which inhibits ovulation and prevents conception. This method provides added benefit to women suffering from conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome, dysmenorrhea and heavy menstrual bleeding. It regulates menstrual cycle in women with PCOS and decreases bleeding in women suffering from HMB. (2)
These pills are taken for 21 days every day at the same time, with a seven-day pill free interval. There is withdrawal bleeding during this phase and the pills are taken after seven days from a new pack. Combined oral contraceptives reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by 50 percent. However, it may increase the risk of cervical cancer as the use of barrier contraceptives is decreased which increases the exposure to human papilloma virus (HPV). (3)
- Barrier contraception
Barrier contraception prevents the sperm from reaching the egg released from the ovary and prevents conception. It also prevents the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases and provides added protection.
Barrier contraception can be provided by various modes like spermicide, sponges, cervical cap, diaphragm in females and condoms in males. (4)
Condoms- These are usually latex barriers that prevent the sperm from reaching the egg. Its role in preventing STI’s is more pronounced as compared to its function as a contraceptive. The incidence of cervical cancer increases when the use of this barrier contraceptive is decreased as it reduces the risk of transmission of HPV. (5)
Spermicide- As the name indicates, spermicide kills the sperms or makes it inactive. The dysfunctional sperms cannot penetrate the egg; hence fertilization does not occur. It can be used with or without barrier contraceptives, as per convenience. It contains nonoxynyl-9 which has spermicidal activity. It is applied in the vagina sometime before intercourse and may cause burning and local irritation in some women. (6)
Sponge- This is a soft sponge that contains spermicide. It is inserted in the vagina, on the cervix and prevents the sperms from entering the uterus. The spermicide slows the sperm and disables it. It is cheap and easily available, however; it’s not commonly used as better options of contraceptives with better efficacy are available. (7)
Cervical caps- This is usually made up of rubber and is placed over the cervix. Like most of the barrier contraceptives, it prevents the sperm from entering the uterus. It can be used for a period of one year if cleaned and maintained properly. It can be used with a spermicide for maximum effect and is supposed to be kept in place for at least 6 hours after intercourse. (8)
Diaphragms- These are like cervical caps which are made up of latex or silicon. These are placed onto the cervix and can be used with a spermicide for better results. It may not be ideal for women who’ve recently given birth or have gained weight as there may be size differences. It must remain intact for up to six hours after intercourse. (9)
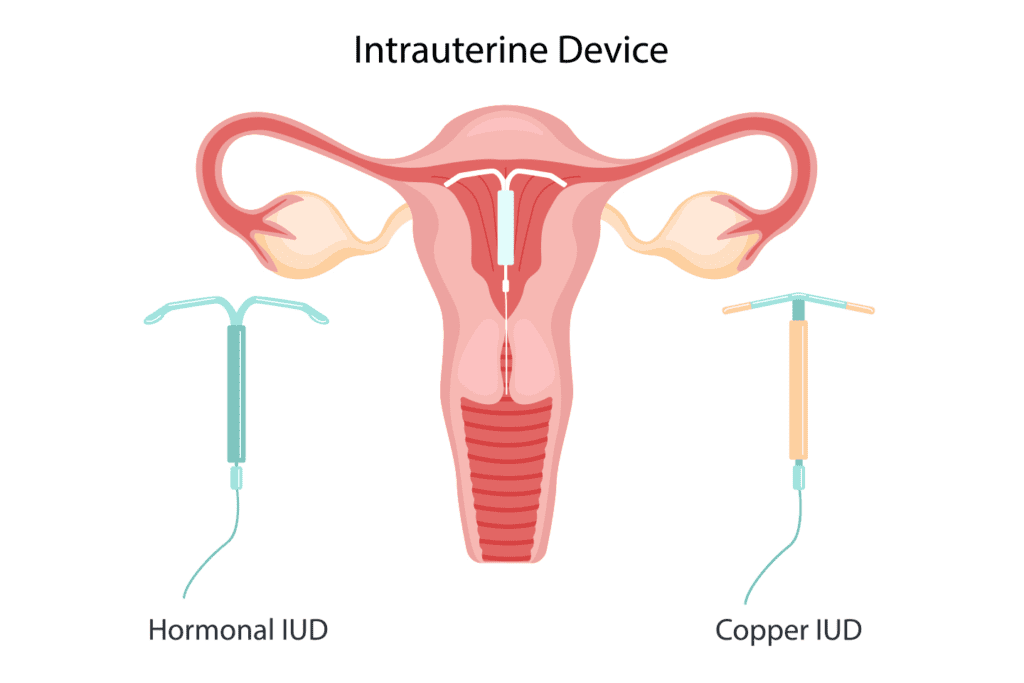
- Intrauterine system
This is a T-shaped device that is placed inside the uterus. This is a long-term method of contraception and provides instant reversal of fertility. It has 99 percent success rate which makes it the contraceptive choice for most women. It is ideal for women who want a long-term contraceptive choice. It releases progesterone locally which thickens cervical mucus and causes thinning of uterine lining which prevents implantation. This contraceptive device is inserted by a physician and is functional for three to four years depending on the brand.
It is helpful for women having heavy menstrual periods as it makes the periods lighter and pain free. However, it may cause irregular periods in the first few months following insertion. Intrauterine system does not provide protection against STIs hence added protection must be used for its prevention. (10)
- Intrauterine device
This is also a T-shaped copper device which is inserted in the uterus by a physician. It releases copper which thickens cervical mucus and causes local atrophy which prevents implantation. It is 99 percent effective in preventing pregnancy. This device provides long term contraception and can remain functional for five to ten years depending on the brand.
There is a risk of infection with copper IUD which must be treated promptly or may lead to pelvic inflammation, and it may cause heavy menstrual bleeding in some women, following its insertion. It has prominent advantages like long term contraception, no induced hormonal changes and is safe to use for breastfeeding mothers. (11)
- Hormone implants
This is a small, rod-shaped contraceptive device that is inserted in the medial side of the upper arm and provides long term contraception. It is efficacy is 99 percent. It is a hormonal device hence; it releases progestin which prevents ovulation, thicken cervical mucus and hinders the access of sperm to the egg and causes thinning of uterine lining which prevents implantation.
There are temporary side effects associated with this like spotting in the first few months, weight gain, acne and breast soreness all of which are due to progesterone release in the blood stream. The benefits however attract the consumers as this contraceptive device is effective unto three years, does not interfere with breast feedings, great option for women who cannot keep up with the daily intake of oral contraceptive pills, decreases heavy menstrual bleeding and pain. (12)
- Natural methods of contraception
This is a natural method of contraception which can be maintained by women by simply monitoring their fertility signs throughout the menstrual cycle. It can be learned by the female by observing her temperatures and fluids coming from the vagina. Added contraceptive cover can also be used during the period of ovulation and for prevention of transmission of STIs. (13)
- Surgery
Couples that have concluded their family planning can opt for surgical options of contraception. These include tubal ligation in females and vasectomy in males.
Tubal ligation- This refers to ligation and tying of fallopian tubes by a suture or clip which disrupts the connection of the uterus and ovaries. This prevents the sperm from reaching the eggs and prevents pregnancy overall. This method is 99 percent effective and is irreversible. This can be done by laparoscopy or laparotomy. (14)
This is a highly convenient method of contraception which does not interfere with hormone release. It also decreases the risk of ovarian cancer by 40 percent. The drawback of this method is that some women may regret their decision and may want to reverse their fertility.
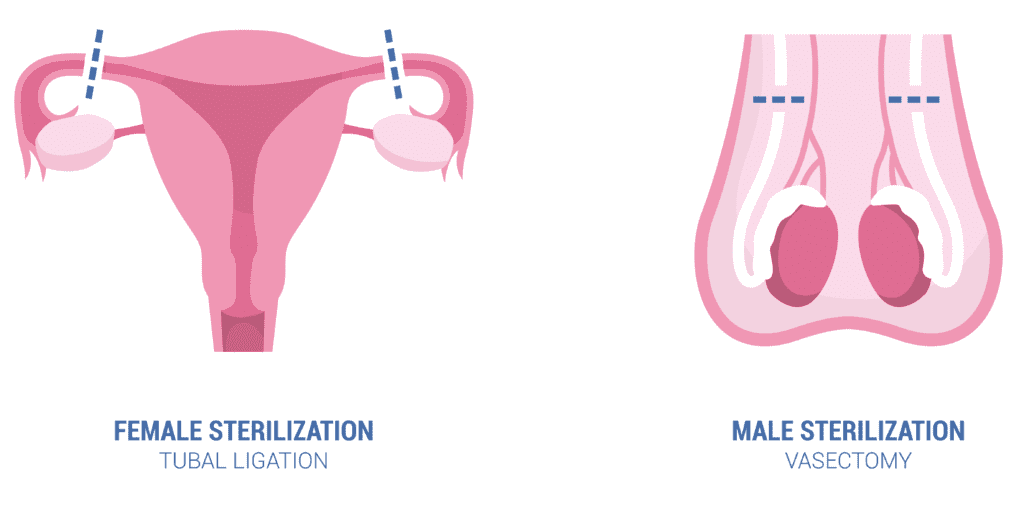
Vasectomy- This refers to a method that involves ligation and dissection of tubes that carry sperms. This obliterates the supply of sperms to semen and prevents conception as a result of intercourse. This is also 99 percent effective and irreversible.
The side effects include surgical site infections in some cases and blood in semen. The benefits are greatly to the females as they don’t have to attain contraceptive protection except for the use of condoms to prevent STIs. Some men may have concerns to regain their fertility which is a major drawback of this method. (15)
Emergency contraception
As the name suggests, this is a method of contraception which is for women who have unprotected sexual intercourse, doubted contraception failure, sexual assault or incorrect application or use of contraception. This must be used within 5 days following intercourse. It acts promptly and prevents pregnancy. There are two options available for emergency contraception, copper IUD and emergency contraceptive pills. The emergency contraceptive pills recommended by WHO are ulipristal acetate, levonorgestrel and combined oral contraceptives. (16)
Ulipristal acetate– a non-hormonal medication that hinders the effect of hormones that facilitate conception.
Levonorgestrel– These pills are available without prescription. It works by interrupting the implantation of the blastocyst on the uterine wall.
Combined oral contraceptives- These can be used as emergency contraception, but the method of intake may differ. It is taken as two pills twelve hours apart and can be taken up to five days of unprotected intercourse for maximum effect. (17)
There are no age limitations or health contradictions for emergency contraception.
Failure of contraception
There is no method of contraception that has a 100 percent success rate. The maximum success rate observed is 98-99 percent. Most people fail to follow instructions which leads to conception. The manufacturers’ guide and doctor’s instructions are very important to follow for proper effect.
The efficacy of contraceptives is user dependent and the incidence of failure corelates with poor compliance and incidental breaks. (18)
Importance of contraception
Worldwide health organizations have been proactive in spreading awareness regarding contraceptive methods amongst women. This is fundamental in reducing the rate of unwanted pregnancies and pregnancy-related mortality in both the mother and child. The economic burden of unintended pregnancy can be overwhelming for couples and the consequences are faced by the progeny where they are deprived of basic educational and health facilities.
The contraceptive methods which are greatly advocated for are the long-acting reversible contraceptives. These are ideal for women who seek long term contraception and show great compliance to these methods. Females who have completed their family or do not wish to extend it further can go for tubal ligation which is an irreversible method of attaining contraception. (19)
Risks of contraceptives
The benefits of contraceptive methods supersede the potential risks in certain conditions, however, there are certain medical states which are contradictory to the use of these methods. The medical eligibility criteria (M.E.C.) outline the W.H.O. guidelines which ensure safe use of contraceptives. For instance, the absolute contradictions of oral contraceptive pills include hypertension, breast cancer, ischemic heart disease, migraines with aura, endometrial cancer and more. When the use of these medications is bypassed by these guidelines, it ensures safe practice and minimizes health risks. (20)
The benefits of contraceptive methods supersede the potential risks in certain conditions, however, there are certain medical states which are contradictory to the use of these methods. The medical eligibility criteria (M.E.C.) outline the W.H.O. guidelines which ensure safe use of contraceptives. For instance, the absolute contradictions of oral contraceptive pills include hypertension, breast cancer, ischemic heart disease, migraines with aura, endometrial cancer and more. When the use of these medications is bypassed by these guidelines, it ensures safe practice and minimizes health risks. (20)
This article summarizes a significant aspect of female reproductive health. Contraception is still considered as a taboo in Pakistan and women hesitate to make their choices. This may partly be due to the lack of knowledge regarding the options that are available. There are various options available now and every individual has the freedom to select the best method according to their needs. Contraception facilitates women to prioritize their health and life choices and provides autonomy towards health and career.





















