What is PCOS?
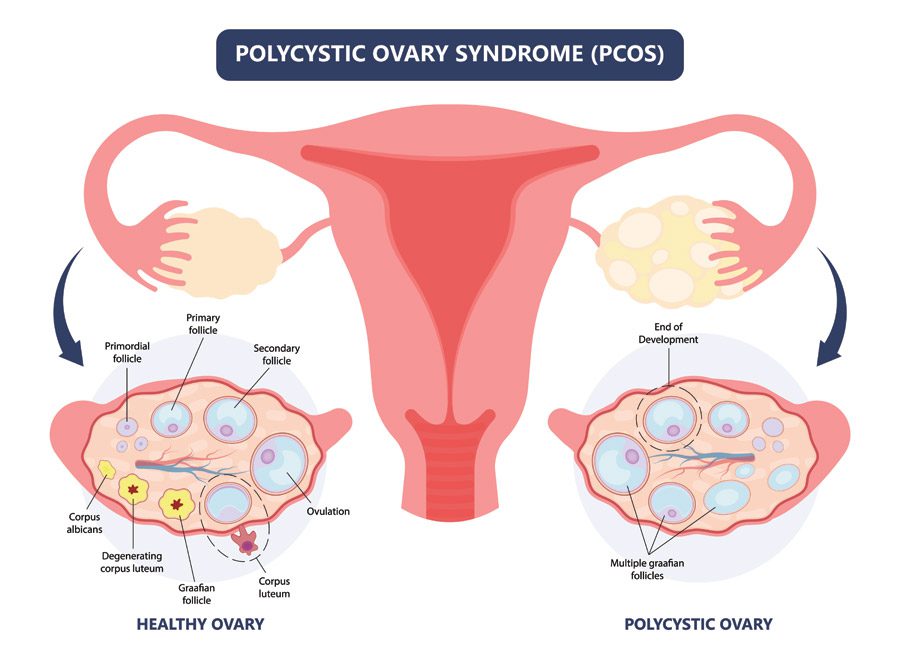
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder found in females of reproductive age. It is predominated by a triad of presentation which includes hyperandrogenism, hirsutism and polycystic ovaries. These females experience anovulatory or missed cycles and often present with infertility.
This disorder affects the ovaries which produce estrogen and progesterone. The cyclical production of these hormones enables the ovaries to release an egg by the process of ovulation. The egg, if fertilized by the sperm results in conception. Hence, the process of ovulation is the key to fertility which is impaired in females suffering from PCOS.
What causes it?
The exact cause of PCOS is not determined but there are some important factors that are considered to play a vital role in the pathogenesis of the disease. Insulin resistance, family history, increased level of androgens and inflammation are considered to be important factors.
Insulin resistance
This refers to the decreased effect of insulin on peripheral tissues and one cause of this is obesity. Insulin resistance causes increased production of androgens (male hormones) from the ovaries. Androgens are normally secreted by the ovaries and adrenal glands but cause clinical symptoms when produced in excess. These include hirsutism and acne. When there is persistent insulin resistance there is a great chance of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is an important contributor in causing PCOS. Eating an improper diet focused on carbs and calories with lack of exercise and energy consuming tasks leads to weight gain which directly leads to hormonal disturbance and PCOS. Focusing on a healthy diet and daily exercise is the first line of treatment for this disease which further signifies its importance.
Family history
Women with PCOS have 50% chances of having an immediate female relative with the same disease. Genes and family history have an important role in the development of this disease.
Hormones
The two most important hormones involved in the development of PCOS are androgens and insulin. These hormones are normally produced in humans in a regulated amount but when produced in excess, they prevent ovulation and disrupt menstrual cycle. Obesity increases the production of these hormones hence an important factor in causing this disease.
How do patients present?
PCOS can be completely asymptomatic in some patients and may come to attention when the patient has irregular cycles or difficulty with getting pregnant. The most common presenting symptoms are,
- Irregular periods
This refers to the absence of regular periods or missed cycles. Some women have less than eight cycles or less per year.
- Hair growth
About 70% of women with PCOS have excessive hair growth on their face and other regions of body. This is because of high levels of androgen in the body. This excessive hair growth is called hirsutism.
- Acne
The effect of elevated androgens also results in oily skin and acne.
- Weight gain
Insulin resistance is a major cause of the resulting weight gain that occurs in patients with PCOS.
- Infertility
As explained earlier, whenever the process of ovulation does not occur normally and the egg is not released, fertilization cannot occur.
- Depression and anxiety
Depression and anxiety are common symptoms of PCOS. It is mostly estimated that this is due to hormonal changes, but further research is required. Some women have also been reported to suffer from eating disorders and all these side effects must be assessed by doctors to provide adequate help.
- Sleep troubles
Women with PCOS tend to be obese and are more likely to have sleep apnea which causes breathlessness in sleep. This results in disturbed sleep and fatigue which aggravates bad mood.
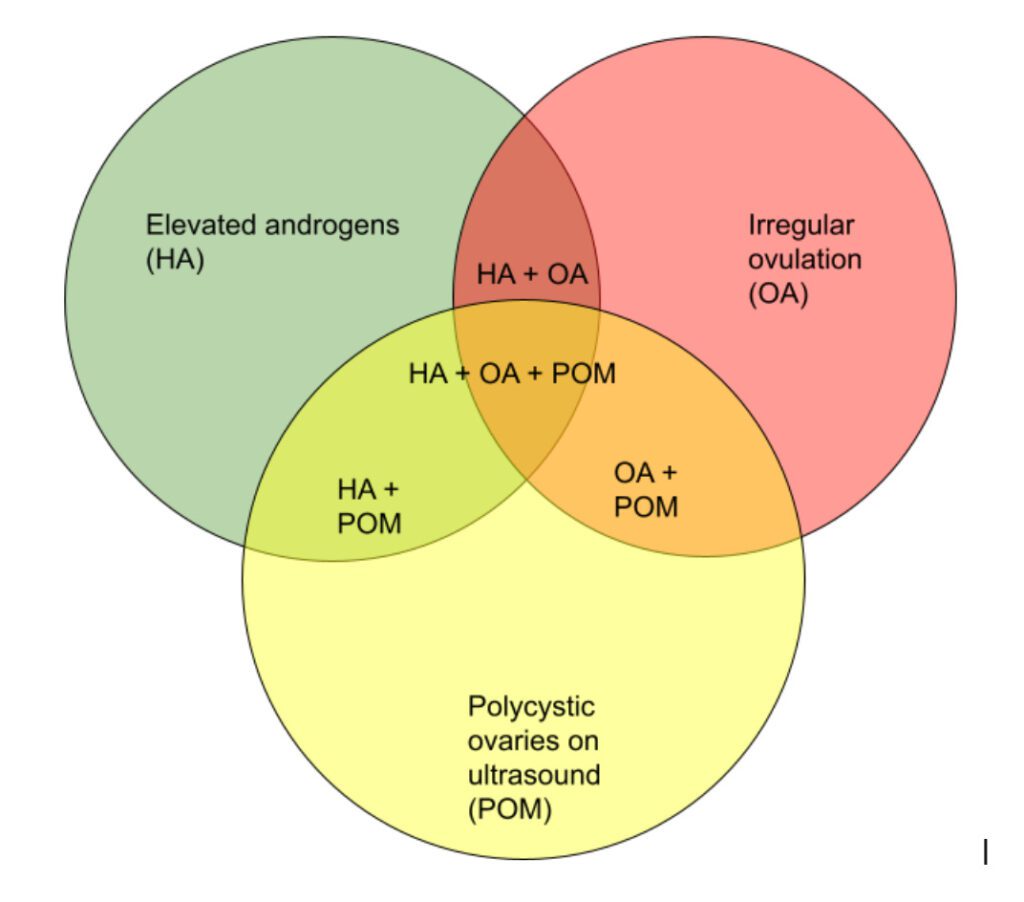
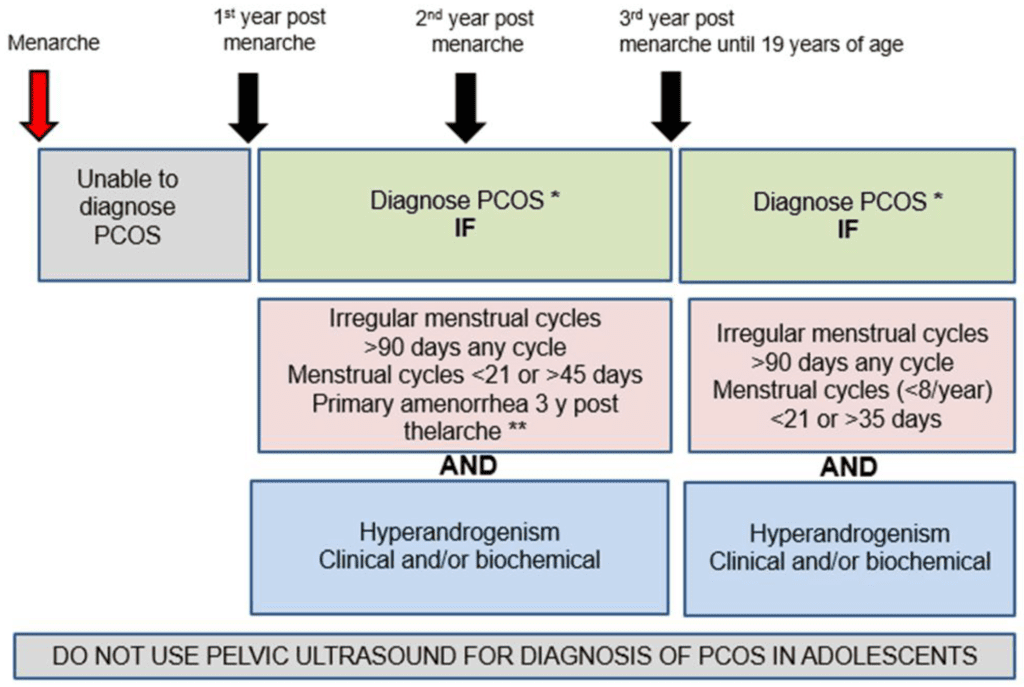
How is it diagnosed?
PCOS is a clinical disease and is best diagnosed based on history and examination. A thorough history about menstrual cycle, weight gain and skin manifestations like excess hair growth on the body, acne and alopecia. The doctor may inquire about the family history as there is a close genetic relation observed.
Other than this, a pelvic ultrasound to see for cysts in the ovaries is also done for diagnosis. Rotterdam criteria is used to diagnose this disease and is based on three factors
- Androgen excess- This can be measured and checked via labs and can be appreciated clinically in the form of acne and hirsutism.
- Ovulatory dysfunction- This can be assessed by the regularity of periods and a mid-cycle check of progesterone.
- Polycystic ovaries- These are cysts caused by incomplete ovulation when there is a failure of the mature follicle to release an egg and it forms a cyst.
It is very important to rule out other important causes of such symptoms like adrenal and thyroid disorders. For this, blood tests are done to be certain about the cause.
Treatment of PCOS
PCOS does not have a definitive treatment, but the symptoms can be managed. There is a range of symptoms that are presented and can be treated according to severity.
Lifestyle changes
The most initial and important step in treating PCOS is to focus on lifestyle changes. These changes are focused on diet and exercise. In overweight females, weight loss can improve the overall outcome of the disease and may prevent from the future complications of this disease. The ideal BMI is between 18.5-24.5.
The diet must be focused on whole foods and fresh protein. Processed food intake increases weight gain and must be avoided overall.
Medication
Different medications can be helpful in treating the symptoms.
- Irregular menstrual cycle – Oral contraceptives are best used for making the menstrual cycle regular. These are taken from the first day of the cycle for 21 days (about 3 weeks) with a seven-day pill-free interval. The use of OCPs provides an added effect of prevention of endometrial cancer with regular cycles every month.
- Infertility – Women with PCOS who are trying to conceive can use clomiphene which induces ovulation and promotes fertility. It is a commonly used drug and may be the first recommended drug for women who are aiming to conceive.
- Another drug, letrozole, is used to induce ovulation and has been successful. It works by blocking estrogen production and increasing follicle stimulating hormone which promotes ovulation. The use of this drug is off label which means that FDA has not approved it for this purpose but its role in fertility has been widely studied and has been proven to be as successful as clomiphene.
- Hirsutism and male pattern hair loss – The most effective first line treatment of hirsutism and acne is the use of oral contraceptives. Electrolysis and laser treatments are effective for mild cases. Eflornithine is a cream that can slow down the growth of excess facial hair, however, it does not remove the already existing hair. Some antiandrogens can also be given to treat hirsutism like cyproterone acetate, spironolactone, flutamide and finasteride. However, these are contraindicated in certain conditions like pregnancy and must be prescribed with contraceptives in sexually active females.
Surgery
If lifestyle changes and medications are not effective, then laparoscopic ovarian drilling can be done. It is a procedure where androgen releasing tissue in the ovaries is destroyed using laser or hot needle. This helps in regulating the menstrual cycle and in conception. (15)
Take away points
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a condition which dysregulates the hormones in the body and causes failure of ovulation.
- It is harder to get pregnant and there are raised levels of androgens in the body which causes facial hair growth and acne.
- The patient presents with a triad of classical symptoms which are hyperandrogenism, anovulatory cycles and polycystic ovaries. The symptoms and severity vary amongst patients.
- PCOS does not have a definitive treatment and is treated symptomatically. The first step to treatment is weight loss, diet and exercise.
- Ovulation induction with medication can help with difficulty in getting pregnant.
- There are long term complications associated with this disease like obesity, diabetes, heart problems, endometrial cancer, sleep apnea, cholesterol and blood fat abnormalities.
- Maintaining a good BMI, eating a healthy diet and daily exercise are the best ways to keep this disease under control. These practices improve the symptoms overall.





















